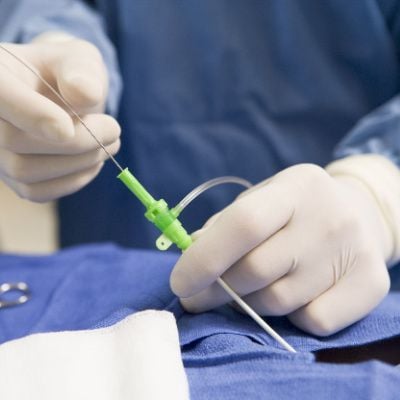
 Cardiac catheterization, a cornerstone of modern cardiology, is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that provides invaluable insights into the heart's structure and function. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the purpose, procedure, applications, and significance of cardiac catheterization in cardiovascular care.
Cardiac catheterization, a cornerstone of modern cardiology, is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that provides invaluable insights into the heart's structure and function. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the purpose, procedure, applications, and significance of cardiac catheterization in cardiovascular care.
Understanding Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into the blood vessels leading to the heart. Typically performed in a specialized cardiac catheterization laboratory, this procedure allows healthcare providers to directly visualize and assess the heart's chambers, valves, and blood vessels.
Indications for Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is indicated for various clinical scenarios, including:
-
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): To assess the extent and severity of blockages in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle.
-
Valvular Heart Disease: To evaluate the function of heart valves and assess the need for repair or replacement.
-
Congenital Heart Defects: For the diagnosis and treatment of structural abnormalities present from birth.
-
Heart Failure: To assess cardiac function and identify contributing factors.
-
Unexplained Chest Pain: To investigate the cause of chest pain when other diagnostic tests yield inconclusive results.
The Cardiac Catheterization Procedure
-
Preparation: Before the procedure, the individual receives a local anesthetic to numb the insertion site, usually in the groin or arm. In some cases, sedation may be administered to help the patient relax.
-
Catheter Insertion: A catheter is carefully threaded through the blood vessels, guided towards the heart under fluoroscopic imaging. The catheter's journey allows for the injection of contrast dye, which enhances visibility on X-ray images.
-
Imaging and Visualization: As the contrast dye fills the blood vessels and heart chambers, real-time X-ray images (angiograms) are captured. These images provide a detailed map of the heart's anatomy and highlight any abnormalities.
-
Pressure Measurements: Specialized sensors on the catheter enable the measurement of pressure within the heart's chambers and blood vessels. This information aids in assessing cardiac function and identifying areas of concern.
-
Optional Interventions: In addition to diagnostic assessments, cardiac catheterization allows for certain therapeutic interventions. These may include angioplasty to open narrowed arteries, stent placement to maintain vessel patency, or valve repair procedures.
Applications in Coronary Artery Disease
-
Assessing Coronary Blockages: Cardiac catheterization is a gold standard for evaluating the severity and location of coronary artery blockages. This information guides treatment decisions, such as the need for angioplasty or bypass surgery.
-
Coronary Angiography: By injecting contrast dye into the coronary arteries, healthcare providers can visualize blood flow, identify blockages, and assess the overall health of the coronary arteries.
-
Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR): FFR, measured during cardiac catheterization, assesses the impact of a blockage on blood flow. It helps determine whether a blockage requires intervention.
Valvular Heart Disease
-
Valvulography: Cardiac catheterization provides a detailed view of heart valve function. Valvulography involves injecting contrast dye to visualize the movement of heart valves and identify abnormalities such as regurgitation or stenosis.
-
Transcatheter Valve Interventions: In some cases, cardiac catheterization allows for transcatheter interventions to repair or replace heart valves without the need for open-heart surgery.
Complications and Considerations
While cardiac catheterization is generally considered safe, like any medical procedure, it carries some risks. These may include bleeding at the catheter insertion site, allergic reactions to contrast dye, and rare complications such as blood vessel injury or infection. Healthcare providers carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks, ensuring that the procedure is appropriate for each individual.
Post-Procedure Care
After cardiac catheterization, individuals are typically monitored for a few hours to ensure stability. The insertion site is monitored for signs of bleeding or infection. Patients receive detailed instructions on post-procedure care, including limitations on physical activities and the management of any discomfort or bruising at the catheter insertion site.
Conclusion
Cardiac catheterization stands as a pivotal tool in the diagnosis and treatment of a wide array of cardiovascular conditions. From unraveling the mysteries of coronary artery disease to assessing the intricate dance of heart valves, this procedure provides healthcare providers with a front-row seat to the cardiovascular symphony. As technology advances and our understanding of cardiac health deepens, cardiac catheterization continues to be a dynamic and indispensable component of cardiovascular care, contributing to the precision and efficacy of interventions aimed at preserving and enhancing heart health.
Disclaimer:
The information on this website is provided for educational and information purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult with a licensed medical provider and follow their recommendations regardless of what you read on this website. If you think you are having a medical emergency, dial 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. Links to other third-party websites are provided for your convenience only. If you decide to access any of the third-party websites, you do so entirely at your own risk and subject to the terms of use for those websites. Neither Paul H. Nguyen, MD, MS, nor any contributor to this website, makes any representation, express or implied, regarding the information provided on this website or any information you may access on a third-party website using a link. Use of this website does not establish a doctor-patient relationship. If you would like to request an appointment with a health care provider, please call our office at (815) 758-7700.


